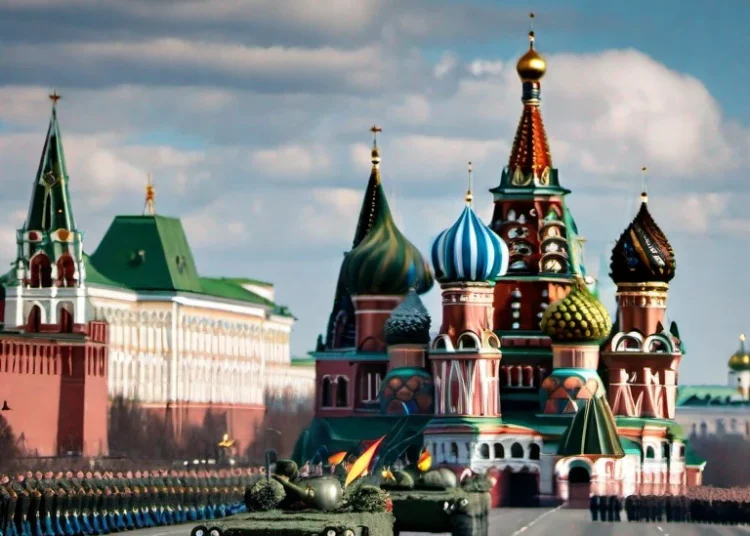
Russia, a nation steeped in rich history, has experienced its fair share of turmoil. From the fall of the Soviet Union to the rise of Vladimir Putin’s regime, political, economic, and social changes have shaped the country’s trajectory. Today, there are concerns regarding the potential for a new civil war in Russia. In this investigative article, we will closely examine the signs that may indicate whether Russia is on a perilous path towards internal conflict.
Political Polarization
One of the primary indicators of a brewing civil war is intense political polarization. In recent years, Russia has witnessed growing ideological divisions leading to increased tensions between opposing factions. Dissent against the Kremlin’s policies, restrictions on civil liberties, and allegations of corruption have given rise to street protests and opposition movements.
While these expressions of discontent may not fully reflect the sentiment of the entire nation, they are indicative of the simmering discontent among certain segments of Russian society. Such polarization could further escalate if left unaddressed, potentially amplifying the risk of a deepening rift and sparking violent clashes.
Suppression of Dissent
The suppression of dissenting voices plays a significant role in exacerbating internal tensions within a nation. In recent years, Russia has witnessed a tightening grip on freedom of expression, independent media, and civil society organizations. Numerous reports indicate the stifling of opposition groups, arbitrary arrests, and silencing of critical voices.
The erosion of democratic principles and the shrinking space for dissent can fuel grievances and contribute to an escalation of conflict. The absence of open dialogue and the perception that legitimate grievances are not being addressed by the government could push discontented factions towards more radical measures.
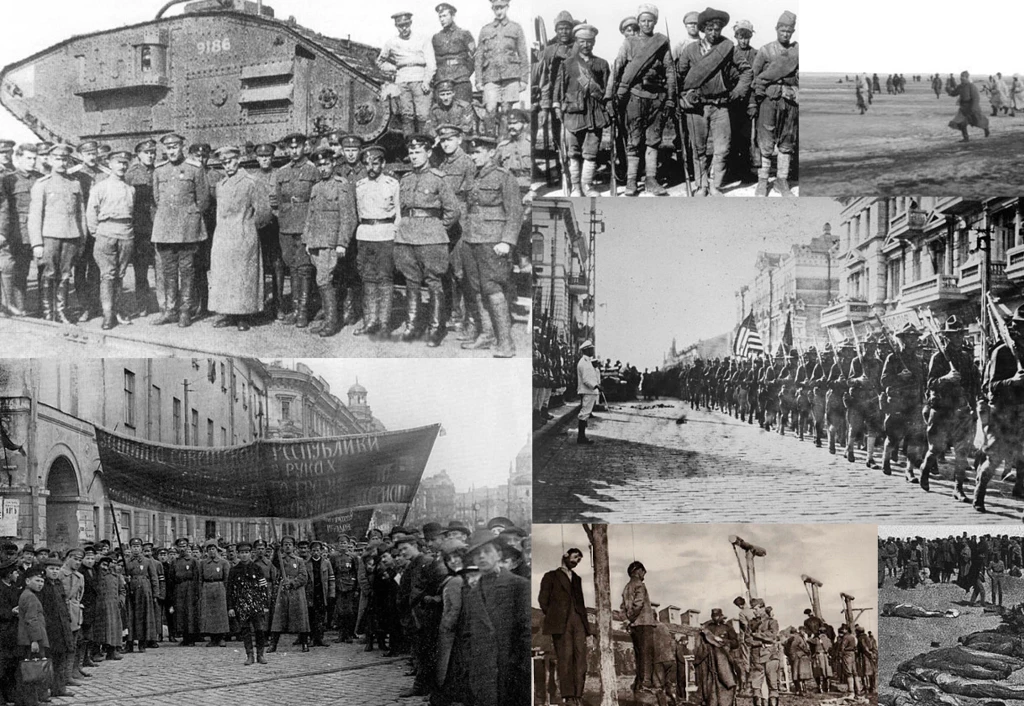

Regional Conflicts and Ethnic Divisions
Russia’s vast territory is home to numerous ethnicities and regional divisions. Stirrings of instability within certain regions, such as Chechnya and Crimea, increase the risk of wider conflict. Nationalist sentiments and an increasing focus on ethnic identity have the potential to heighten societal divisions and ignite clashes between different groups.
Additionally, economic disparities between affluent urban centers and neglected regions exacerbate grievances. Neglect of local interests and the perception of uneven distribution of resources can create a breeding ground for social unrest, intensifying the possibility of a civil war.
Economic Instability
Economic instability often serves as a catalyst for social unrest and political upheaval. International sanctions, declining oil prices, and ongoing geopolitical tensions have deeply impacted Russia’s economy. The COVID-19 pandemic has further strained the nation’s resources, contributing to rising unemployment, inflation, and poverty rates.
Diminishing economic opportunities, coupled with growing income inequality, can breed frustration and fuel social discontent. An economically strained population may demand radical change, potentially escalating the risk of widespread destabilization and violence.
Final Thoughts
While it is crucial to remain cautious when making predictions about the future, the signs mentioned above indicate potential risks that Russia currently faces. Political polarization, suppressing dissent, regional conflicts, ethnic divisions, and economic instability all contribute to an environment that could worsen if not addressed promptly.
It is imperative for the Russian government to recognize the signs and take proactive measures to address the deep-rooted issues within society. Fostering inclusive governance, promoting dialogue, and addressing economic disparities can help alleviate the tension and reduce the likelihood of a new civil war.
However, only time will truly reveal Russia’s trajectory. As concerned individuals, we must closely monitor these signs while advocating for peaceful solutions and encouraging an open exchange of ideas to avert any potential crisis.